-
1) What is Soil Stress ?
-
2) Example
-
3) Comparison of Results

4. Soil Stress
In this lecture, We will learn about the concepts and principles of soil stress. Through thus We will learn about the two major stresses which are generated in the soil, i.e. initial and induced stress. We will also see the different theories/methods to calculate soil stress based on the loading type. In order to comprehend the Soil stress utilizing GTS NX software, we will model the strip load on the elastic ground.
Chapter 1) What Is soil stress?
- Introduction to nonlinear numerical (FEM) analysis
- Details about types of soil stress
- different theories/methods to calculate soil stress based on the footing type
Chapter 2) Example
- Modelling, boundary condition setting, applying load using Midas GTS NX software to simulate the Strip load on the elastic ground.
- Analysis and see the results for the same.
Chapter 3) Comparison of results.
- Compare the results with those obtained manually and using the program.
Summary
Stress in the ground can generally be divided into intrinsic (initial) stress and induced stress. Intrinsic stress refers to the stress in a natural state that the ground has through gravity or geological action.
This is the stress before the construction is carried out and is also called 'initial stress’.
On the other hand, induced stress refers to stress caused by artificial construction activities such as foundation loading, soil, and excavation.
Changes in external force due to construction activities cause additional stress along with disturbance of initial stress. Therefore, the underground stress is expressed as follows.
Underground stress = initial stress + induced stress

1) Initial Stress
Vertical stress within the ground can be defined as the effect of self-weight, despite geological action, for ground using the following equation.
The static horizontal stress is expressed as a ratio (Ko ) to the vertical stress.

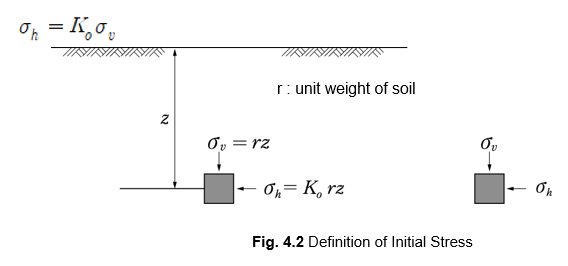
𝐾o of the above equation is a horizontal stress coefficient, and 𝐾o of loose sand or slightly compressed clay is less than 1. Jacky (1944) proposed the following equation.

The 𝐾o of dense sand or excessively dense rigid clay is usually greater than 1. 𝑀𝑎𝑦𝑛𝑒 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝐾𝑢𝑙ℎ𝑎𝑤𝑦 (1982) proposed the following equation.

If the horizontal displacement of the homogeneous isotropic rock (deposited rock) is negligible in the elastic range, the elastic theory establishes the following equation.

2) Induced Stress
Induced stress is the stress added to the ground by an external load and In theoretical soil mechanics, the ground is assumed to be a semi-infinite, isotropic, elastic medium which is obtained by using the theory of elasticity and Airy's Stress Function. Depending on the loading conditions, the following solutions are presented.
- Surface vertical concentrated load (Problem of Boussinesq)
- Surface Line Load (Problem with Flamant)
- Surface shear concentrated load (Cerrutti's problem)
- Surface vertical concentrated load (Mindlin's problem), etc
When the load is distributed in any form, such as a circle or a square, the induced stress can be obtained by integrating the solution of the above basic stress with respect to the load shape and the working area.
